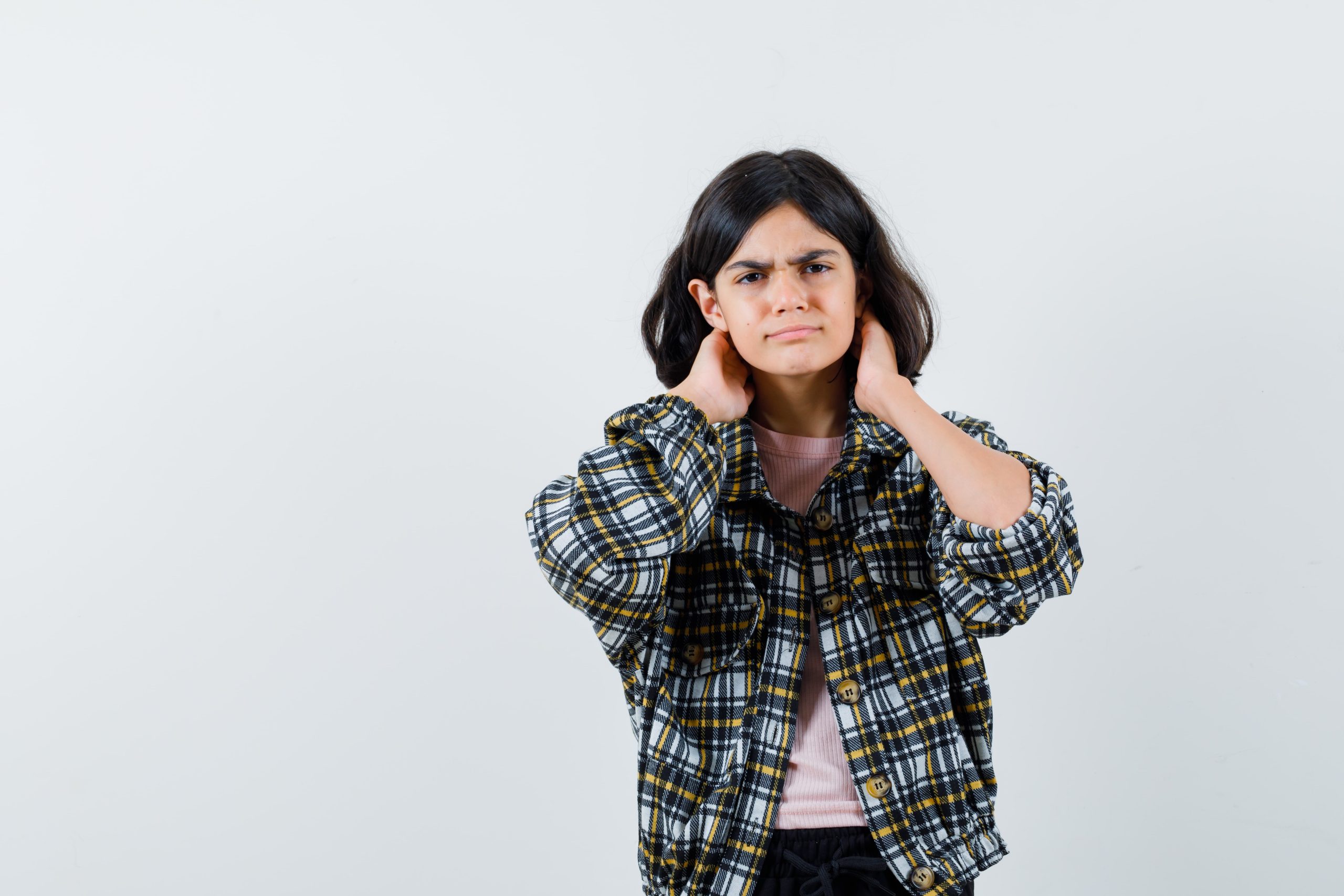
Ear infections can be painful and frustrating, affecting both children and adults. If left untreated, they can lead to serious complications. In this blog post, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and best treatment options for ear infections to help you find relief quickly.
What Causes Ear Infections?
Ear infections, medically known as otitis media, occur when bacteria or viruses infect the middle ear. Common causes include:
- Colds and respiratory infections—Viruses and bacteria from the throat can travel to the ear.
- Allergies—Can cause swelling and block the Eustachian tubes.
- Sinus infections—Increased mucus can trap bacteria in the ear.
- Excess earwax—This can create an environment for bacteria growth.
- Water exposure—trapped water (swimmer’s ear) can lead to infections.
- Weakened immune system—People with weaker immune responses, such as children and the elderly, are more prone to infections.
- Frequent use of pacifiers—In infants, excessive pacifier use has been linked to a higher risk of ear infections.
Symptoms of an Ear Infection
The symptoms may vary depending on the severity and type of infection, but common signs include:
- Ear pain or discomfort (ranging from mild to severe)
- Hearing loss or muffled hearing
- Fluid drainage from the ear (yellow, precise, or bloody discharge)
- Fever (especially in children)
- Dizziness or vertigo
- A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear
- Irritability and trouble sleeping (especially in young children and infants)
Ear infections treatment Options
Treatment for ear infections depends on the cause and severity. Here are the best remedies:
1. Home Remedies for Mild Cases
- Warm Compress—Apply a warm cloth to the ear to reduce pain.
- Olive Oil Drops—Helps soothe irritation (only if the eardrum isn’t perforated).
- Stay Hydrated—Drinking fluids helps clear the Eustachian tubes.
- Rest and Sleep Upright—Helps fluid drain from the ears naturally.
- Garlic Oil—Known for its natural antibacterial properties, it can help ease symptoms.
- Apple Cider Vinegar—A diluted solution may help in cases of fungal ear infections.
2. Medical Treatments
- Antibiotics are prescribed if the infection is bacterial.
- Pain Relievers—Ibuprofen or acetaminophen can ease discomfort.
- Ear Drops—Useful for outer ear infections.
- Decongestants or Antihistamines—Help clear blocked Eustachian tubes.
- Ear Tubes (for recurrent infections)—In some cases, doctors may recommend inserting ear tubes to help with drainage and prevent further infections.
3. When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if:
- Symptoms persist for more than 48 hours.
- Pain becomes severe or unbearable.
- High fever (above 102°F or 39°C) occurs.
- Hearing loss or balance problems develop.
- Ear infections keep recurring frequently, which may indicate an underlying condition.
How to Prevent Ear Infections
- Keep ears dry—use earplugs while swimming.
- Avoid smoking and secondhand smoke—smoke irritates the ear’s lining.
- Practice good hygiene—wash hands to prevent infections.
- Vaccinate—Flu shots and pneumococcal vaccines help reduce risk.
- Breastfeed infants—Breastfeeding for at least six months has been shown to reduce the likelihood of ear infections.
- Manage allergies—Keeping allergies under control can reduce inflammation in the Eustachian tubes.
Final Thoughts
Ear infections can be painful but can be managed effectively with proper treatment. Whether using home remedies or medical treatments, early intervention is key. If symptoms persist, consult a doctor to prevent complications.
Have you experienced an ear infection before? Share your experience or tips in the comments below!
মাথা ঘোরা কমাতে সেরা ৫টি ব্যায়াম